Please contact our sales team.
For a quote on your custom requirements please send us your drawing or specification.
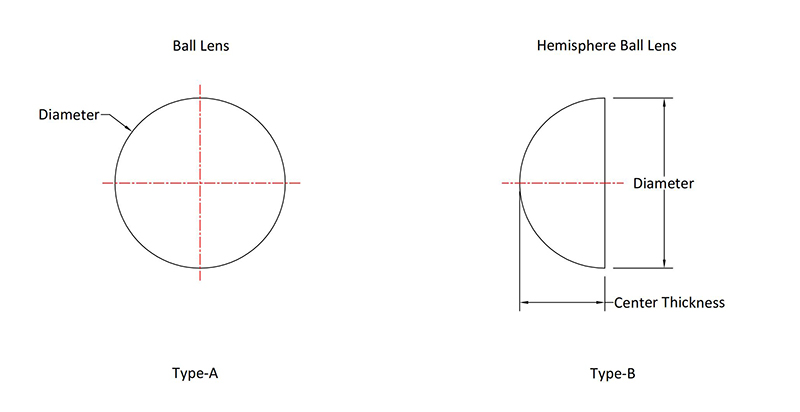
Ball Lenses & Half Ball Lenses
Ball Lenses & Half Ball Lenses
Ball lenses are perfectly spherical lenses, manufactured primarily from a single glass substrate, that can focus or output parallel light, depending on the geometry of the input source. Characterized by the absence of mirror edges, ball lenses have a short back focal length to minimize the distance between the ball lens and the fiber. They are commonly used for coupling between optical fibers, between lasers and optical fibers, and between optical fibers and detectors to improve signal quality in fiber-coupled applications, or as objective lenses in endoscopy, laser measurement systems, and barcode scanning. Ball lenses are rarely used in imaging applications due to their large optical aberration. However, they have very short focal lengths and can be used to make very simple microscopes.
In addition to fiber optic coupling applications, ball lenses are used as objective lenses in endoscopes, laser measurement systems and bar code scanning.
CLZ Optical Co., Ltd. launched a new Online Stock product in 2024, offering a range of stock ball lenses that you can choose and buy high quality ball lenses online anytime, anywhere.
![]()
Please contact our sales team.
For a quote on your custom requirements please send us your drawing or specification.
Custom Options >
Type >
Application of Ball Lenses >
Materials: Optical Glass, Quartz, Sapphire & Ruby, Silicon, Si3N4, Metals, etc..
Dimensions: Diameters 0.3mm to 150mm
1. Optical Coupling
2. Fiber Optics
3. Microscopes
4. Photographers
5. Bearing (mechanical)
Please contact us for discount pricing for stock parts over 10+ and volume/OEM quantities
| Type No. | Data sheet | Diameter (mm) | Material | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-HB030900H | PDF > | 9.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030800H | PDF > | 8.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030600H | PDF > | 6.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030500H | PDF > | 5.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030400H | PDF > | 4.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030300H | PDF > | 3.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030200H | PDF > | 2.00 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens | |
| L-HB030150H | PDF > | 1.50 | Sapphire | Half Ball Lens |
Now Shopping by
Related Categories
Application of Ball Lenses
1. Optical Coupling
A ball lens refracts light at the interface between its surface and the surroundings. Light from a collimated source is bent into a converging cone. The light travels in a straight line inside the lens, then bends again as it exits, converging to a focal point that is usually outside the sphere.
The effective focal length (EFL) of a ball lens is much greater than the back focal length (BFL), which is the distance from the back of the lens to the focal point. For a given lens diameter (for a spherical lens), the focal length of a ball lens is the shortest. This allows the light of a collimated beam to be focused to a smaller diameter than other spherical lenses due to optical invariance. Similarly, a point source of light placed at the focal point will produce a collimated beam out the other side of the lens, and the large ratio of the lens diameter to the focal length (large numerical aperture) allows more light to be captured than other spherical lenses. This makes ball lenses particularly useful for coupling light from lasers to optical fibers or detectors, or from one optical fiber to another, or for use in micro-optical systems. In addition, ball lenses are omnidirectional, and compared to other types of lenses, they only need to be kept centered, thus facilitating the alignment of optical couplers. Ball lenses used for optical coupling are typically small, ranging from 5 mm to 110 microns, with focal lengths ranging from 100 to 250 microns. They are typically made of high-quality optical glass (such as borosilicate glass or quartz glass) or crystal (such as synthetic sapphire) with a refractive index between 1.5 and 1.8. For a given size ball, the higher the refractive index, the shorter the focal length.
2. Fiber Optics
Ball Lenses are often used in fiber optics. Since they have a short focal length, they have a small diameter in the laser beam, making them ideal for focusing all the light from the laser into the fiber core. The numerical apertures of the fiber and lens need to be matched. The fiber can often be in direct contact with the ball, which helps to simplify alignment.
Ball lenses are also used at the output of fiber optic cables to collimate the output beam. Thus, two lenses placed back to back can be used to couple two cables together.
3. Microscopes
Spherical lenses are rarely used in imaging applications due to their large optical aberrations. However, they have a very short focal length and can be used to make very simple microscopes. A 3 mm ball lens can magnify an image 100 to 200 times, while a 1 mm ball lens can produce an image 200 to 350 times larger than actual size.
4. Photographers use ball lenses or “lens balls” to take novel ultra-wide-angle photographs. A ball lens is placed close to the camera and the camera's own lens is used to focus the image through the ball. If the camera is too close to the ball lens, the background around the ball will be completely blurred, and conversely, the farther away from the ball lens, the clearer the background will be.
5. Bearing (mechanical)
The application of ball lenses in bearings is mainly reflected in optical alignment and focusing, as well as special designs to meet the specific needs of bearings.
Optical alignment and focusing: Spherical lenses are used in optical alignment systems in bearings due to their unique shape and optical properties. They can help focus or expand light, ensuring that bearings can maintain precise alignment during operation, thereby improving their operating accuracy and stability. This application is particularly suitable for bearing systems that require high-precision operation, such as precision machinery, optical instruments, etc. 1 Special design to meet bearing needs: In some specially designed bearings, spherical lenses may be used as key components to meet specific functional requirements. For example, in spherical sliding bearings, the spherical design of the lens can match the spherical structure of the bearing to ensure that the bearing seat can work stably and effectively in the application. This design can withstand composite loads dominated by radial loads, and can also withstand axial loads alone, improving the bearing's load capacity and stability.