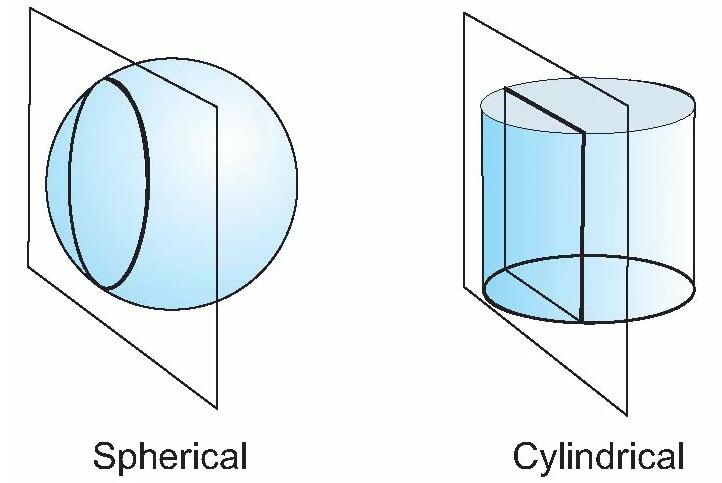
Cylindrical vs Spherical lenses
Sep. 30, 2022
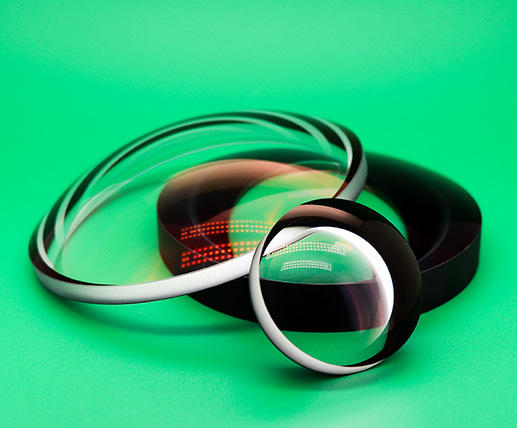
Spherical lenses
Spherical lenses are the most frequently used optical elements, either alone or in various combinations.
A simple lens has two spherical surfaces, the centers of curvature of the connector consists of an optical axis of the lens.
Cylindrical vs Spherical lenses
Imagine a sphere made out of glass and let’s say we cut at any plane completely across the sphere. Our end piece will be a spherical lens, with a flat surface and a curved surface. If we were to illuminate the flat side with a light source, we will see that all of the light is focused to a single point some distance in front of the lens. If we rotate a spherical lens, the position and shape of the focused light wouldn’t change.
Now imagine that, instead of cutting a glass sphere, we cut a glass cylinder. We need to cut the cylinder with a plane parallel to its axis of rotation (that would be the longest axis). We end with a lens that is flat on one side and curved on the other. However, the curve of a cylindrical lens only goes in one direction. Why is that important? Well, because when we illuminate a cylindrical lens, instead of the light focusing into a point it will focus into a line. Not only that, if we rotate the cylindrical lens along the optical axis, the focused line will change its orientation.
Fused silica lenses for F-Theta Lenses
Applications of Cylindrical Lenses
Optical Spectroscopy
Optical spectrometers usually use a cylindrical lens in their design. It is usually placed after a diffractive grating element to focus light into a single line that is incident to a linear photodetector.
Correcting Astigmatism
One of the main applications of cylindrical lenses is in ophthalmology, specifically, to correct astigmatic vision. When a person presents astigmatic vision, it is usually the result of a corneal deformation. An astigmatic cornea will have different focal points at different axes. It is then possible to use a cylindrical lens to change the focal point of one of the axes to overlap the second one.
Laser Beam Shape Correction
Ideally, light emitting from a laser should be a perfect circle; however, semiconductor laser present an elliptic beam profile. So it is necessary to correct the beam profile so we can collimate the beam and couple it to an optical fiber. We can correct such profile by placing a cylindrical lens with its main axis perpendicular to the fast axis of the laser beam.
Laser Scanning Microscopy
They are usually used in combination with acousto-optic deflectors, where the focal point of a variable lens (the acousto-optical elements) can change its position laterally without the use of movable parts. The cylindrical lens corrects the image and helps focus the light spot onto the correct plane for laser scanning microscopy.
Laser Line Scanning
This is a technique that is used to capture the shape of a 3D object into a digital copy. It is particularly useful in manufacturing, prototyping, landscaping, and architecture. This scanning technique measures the deformation of a straight line created by a cylindrical lens when it is incident into a non-flat surface. By using cameras and triangulation, it is possible to measure the changes in the shape of our laser line and therefore estimate the shape of the object that we are measuring.
Plano-Convex Cylindrical Lenses
If you want to know information about custom lenses, please contact us. We will provide professional answers.