Learn more about pyranometers
Oct. 15, 2024
A pyranometer is a radiometer used to measure solar irradiance on a flat surface. It is designed to measure the density of solar radiation above a hemisphere in the wavelength range of 0.3μm to 3μm. A typical pyranometer does not require any power supply to operate. However, recent technological developments include the use of electronics in pyranometers, which require an external power supply.
What does the pyranometer measure?
Pyranometer measure global irradiance in watts per square meter (W/m2). Global irradiance is the amount of solar energy per unit area per unit time, from direct and diffuse sun radiation. Direct radiation, i.e. direct sunlight, is directed from the sun straight to the earth without interference from clouds or atmospheric particles. Diffuse radiation is sunlight scattered by water droplets and air molecules and reflected by buildings, trees, etc. Measuring these two components is critical to understanding the availability of solar energy at a given location. Pyrometer sensors convert global irradiance into an electrical signal that can be measured.
Application of pyranometer
The primary role of the pyranometer is solar monitoring. Solar monitoring measures the intensity, duration and availability of sunlight. Measuring these factors is most commonly used in the following industries:
Solar energy industry
Pyranometers are indispensable in the field of solar energy. They are essential for evaluating the performance of solar panels and photovoltaic (PV) power plants.
With solar monitoring, you can optimize the positioning of solar installations and calculate the potential energy yield.
2. Agriculture
Pyranometers also have a great role to play in optimizing crop growth and irrigation systems. If you know when and how much solar energy is available, you can make better decisions about planting times, and irrigation needs for your crops. In greenhouses, data from sunlight radiometers help control light levels to ensure optimal plant growth.
3. Meteorology and climate science
Measuring solar irradiance is also useful for studying weather patterns and atmospheric conditions. The data from a pyranometer sensor is pivotal in determining long-term weather forecasts and climate models.
4. Architecture and urban planning
It may be helpful for architects to understand solar radiation before they plan their buildings and cities. In this way, they can design buildings that utilize sunlight efficiently. Especially in recent years, solar radiometers can improve the energy efficiency of buildings and maximize the use of sunlight.
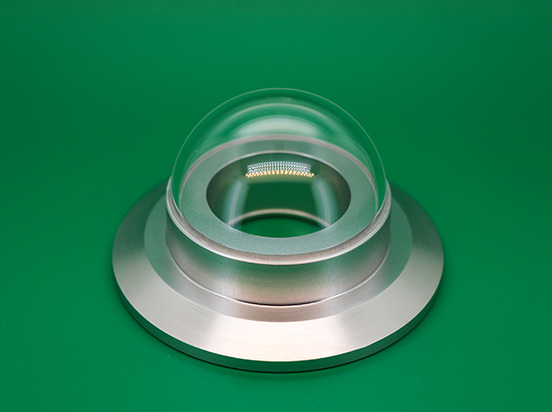
Composition of the pyranometer
The Pyranometer consists of several main components:
1. Optical Dome: The double glass cover is designed to minimize the effect of air convection on the radiation meter. The inner dome is used to cut off the infrared radiation from the outer dome to ensure the measurement's accuracy.
2. Induction element: The induction element is the core part of the total radiation meter.
3. Light shield, meter body, and desiccant: these parts constitute the external structure of the total radiation meter and auxiliary equipment to ensure that the instrument can work properly in various environments and protect the internal structure.
CLZ Optical Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer of optical components, mainly products including spherical lenses, optical domes, optical windows, etc.
Optical Dome is composed of two parallel optical surfaces. Among optics, domes are unique because, unlike any other optical components, the key attribute of the dome is to have no optical effect. Mirrors reflect light, lenses bend light, and domes ideally change nothing. Typically the lead element in an optical system, a dome is often exposed to the environment to resist wind & rain erosion for pyrometers, and as high-pressure viewports in underwater cameras and submersibles.
Please contact us if you are interested in our product!


















